Organizations are increasingly moving their IT infrastructure to the cloud, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is one of the most popular cloud providers. While cloud computing offers many benefits, such as scalability and flexibility, it also introduces new security challenges. New innovations in Cloud security tools are finally catching up to address “context” that prioritizes risks and reduces the operational burden on remediations. It is common for organizations to run five or six security tools, but each tool generates lots of findings or alerts. There is a need to reduce this alert and prioritize risks based on context. This can help organizations ensure the security of their GCP cloud by providing additional layers of protection and visibility into their cloud environments with prioritization of what to fix first that has the highest risk.
This blog will discuss how context-aware cloud security tools can help ensure an organization’s Google Cloud security by looking at all additional context associated with that server, database, etc. Running individual scans like vulnerability, malware, and posture management is now old school. It is time to upgrade your google cloud platform security, and Cloudnosys is one such vendor that provides this capability.
8 Google Cloud Security (GCP) Best Practices to Implement Today!
1. Vulnerability Scanning
One of the most critical security challenges organizations face is the identification of vulnerabilities in their workload and overall cloud infrastructure. Vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, loss of sensitive information, and financial loss. Context-driven Cloud security tools can check if two servers with the same CVSS score have additional risks such as one server may be open to the internet or have PII data attached to it. In that case, these servers are prioritized over others. Today non-context-aware tools cannot perform such functions, hence organizations are left with identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities by manually scanning and merging their GCP resources for known vulnerabilities and configuration errors. By scanning GCP resources, organizations can identify and remediate security issues before attackers exploit them.
2. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM tools can help organizations detect and respond to security incidents by aggregating and analyzing log data from various sources in their GCP environment. SIEM tools can collect and analyze data from GCP services such as Cloud Storage, Compute Engine, and Cloud Logging, as well as third-party tools. SIEM tools can help organizations detect and respond to security incidents such as unauthorized access attempts, data exfiltration attempts, and malware infections. The core issue with SIEM tools is data latency, the complexity of merging, and the normalization of logs, data, transactions, etc. Consider augmenting SEIM tools with Cloud Security Posture Management tools to increase posture upfront in the process.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM tools can help organizations manage user access to GCP resources, enforce strong password policies, and enable multi-factor authentication. IAM tools allow organizations to define roles and permissions for users, groups, and service accounts, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data. IAM tools can also help organizations enforce strong password policies, such as minimum password length, complexity requirements, and password expiration. Multi-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password.
4. Encryption and Key Management
Encryption is a crucial part of cloud security and helps protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Cloud security tools can help organizations encrypt data at rest and in transit and manage encryption keys in a centralized location. Encryption at rest helps protect data stored in GCP services such as Cloud Storage and Compute Engine. Encryption in transit protects data as it moves between GCP services and external networks. Encryption keys can be managed using a key management service such as Google Cloud KMS, which provides a secure and centralized location for key management.
5. Network Security
Google Cloud Security Platform can help organizations monitor network traffic in their GCP environment, enforce firewall rules, and detect and respond to suspicious activity. GCP provides a virtual private cloud (VPC) that allows organizations to create a secure and isolated network environment for their GCP resources. Firewall rules can be used to control access to GCP resources based on source IP addresses, protocols, and ports. Google Cloud security tools can monitor network traffic and detect suspicious activity such as port scans, denial of service attacks, and unauthorized access attempts.
6. Compliance Management
Compliance management is a critical aspect of cloud security, especially for organizations in regulated industries such as healthcare and finance. Cloud security tools can help organizations manage compliance with various regulations and standards, including HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. Compliance management tools can help organizations track and report on compliance requirements, implement security controls, and monitor compliance violations.
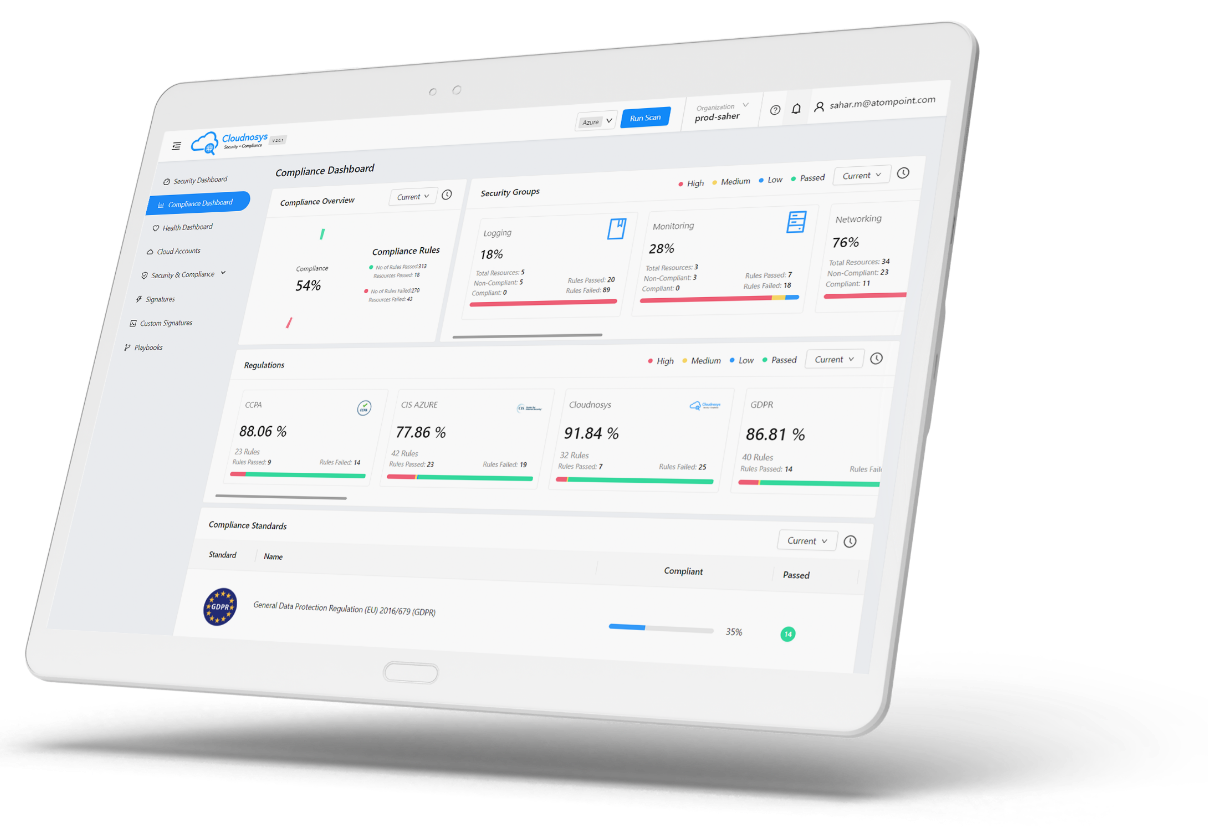
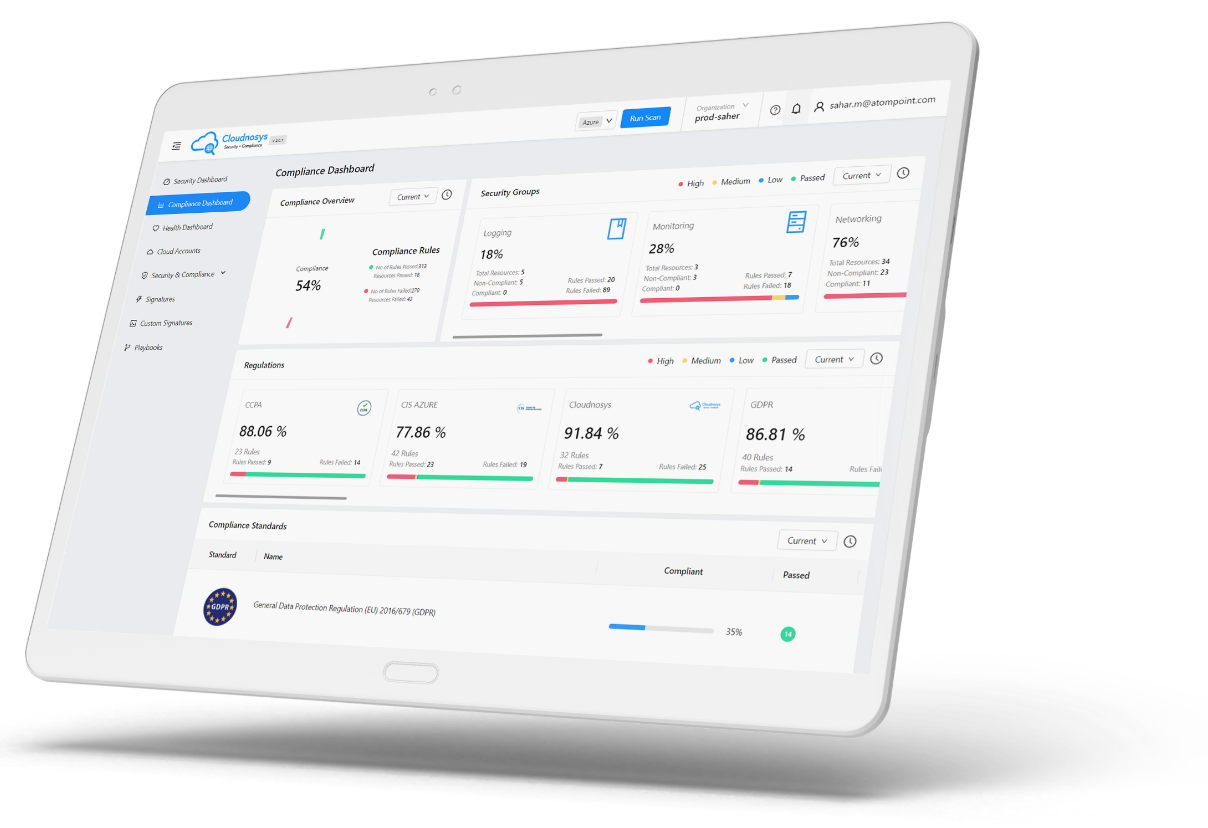
Cloudnosys cloud security and cloud compliance tool is an example of a cloud security tool that can help organizations ensure the security of their GCP cloud. Cloudnosys provides a comprehensive platform for cloud security and compliance, offering features such as vulnerability scanning, compliance management, and configuration management.

7. Cloud Security Posture Management – CSPM
A cloud security posture management (CSPM) strategy is now considered an essential element of a comprehensive cloud security program. It identifies and addresses cloud security risks, and drives the hygiene of cloud service configurations. Also identifying toxic configurations, and analyzing IAM and many other security controls. If you are running a Public cloud, this is a must-have capability, however ideally it should work with your other security tools in helping drive context and prioritize risks.
8. Malware Management
Many organizations think that malware cannot reach cloud storage, bucket, or some attached volume of a virtual machine, as they think their endpoints are protected. This is just not true, we are now discovering malware exists in cloud storage services, and hence you need a malware capability to address these ransomware types of risks. However, malware should not work in a standalone, and it should help drive risk prioritization.